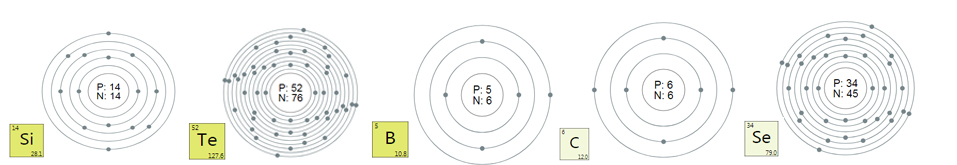
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element, its chemical symbol is
Si, formerly known as silicon. The atomic number is 14, the relative
atomic mass is 28.0855, there are two allotropes of amorphous silicon
and crystalline silicon, belonging to the third period of the periodic
table, the metal-like element of the IVA group. Silicon is also a very
common element, but it rarely appears in nature as a simple substance,
but in the form of complex silicate or silica, which is widely present
in rocks, gravel, and dust. The reserves of silicon in the universe rank
eighth. In the earth's crust, it is the second most abundant element,
constituting 26.4% of the total mass of the earth's crust, second only
to the first oxygen (49.4%).
Application field
1. High-purity single crystal silicon is an important semiconductor
material. A small amount of group IIIA element is added to
monocrystalline silicon to form a p-type silicon semiconductor; a small
amount of group VA element is added to form an n-type semiconductor. The
p-type semiconductor and the n-type semiconductor are combined to form a
p-n junction, which can be made into a solar cell, which converts
radiant energy into electrical energy. It is a promising material in the
development of energy. In addition, the widely used diodes, triodes,
thyristors, field effect transistors and various integrated circuits
(including chips and CPUs in people's computers) are all made of
silicon.
2. Metal ceramics, important materials for space navigation. Ceramic and
metal are mixed and sintered to make a metal-ceramic composite material,
which is resistant to high temperature, rich in toughness, and can be
cut. It not only inherits the respective advantages of metal and
ceramic, but also makes up for the inherent defects of the two. It can
be used in the manufacture of military weapons. The first space shuttle
"Columbia" was able to withstand the high temperature generated by
friction when traveling through dense atmosphere at high speed, thanks
to its shell made of 31,000 silicon tiles.
3. Optical fiber communication, the latest modern communication method.
Pure silica can be used to draw high-transparency glass fibers. The
laser can be transmitted forward through countless total reflections in
the path of the glass fiber, instead of bulky cables. The optical fiber
communication capacity is high. A glass fiber as thin as a hair can
transmit 256 telephones at the same time; and it is not affected by
electricity or magnetism, is not afraid of eavesdropping, and has a high
degree of confidentiality. Optical fiber communication will
revolutionize human life in the 21st century.
4. Silicone organic compounds with excellent performance. For example,
silicone plastic is an excellent waterproof coating material. Spraying
silicone on the walls of the subway can solve the problem of water
seepage once and for all. Coating a thin layer of silicone plastic on
the surface of ancient cultural relics and sculptures can prevent moss
from growing and resist wind, rain, and weathering. The Monument to the
People's Heroes on Tiananmen Square is treated with silicone plastic, so
it will always be white and fresh.
5. Due to the unique structure of organic silicon, it combines the
properties of inorganic materials and organic materials. It has basic
properties such as low surface tension, low viscosity-temperature
coefficient, high compressibility, and high gas permeability. It also
has high and low temperature resistance, electrical insulation, and
resistance. Excellent properties such as oxidation stability, weather
resistance, flame retardancy, water repellency, corrosion resistance,
non-toxicity and tastelessness, and physiological inertness. It is
widely used in aerospace, electronic and electrical, construction,
transportation, chemical, textile, food, light industry, medical, etc.
In the industry, silicones are mainly used in sealing, bonding,
lubrication, coating, surface activity, mold release, defoaming, foam
suppression, waterproofing, moisture-proof, inert filling, etc. With the
continuous growth of the number and variety of silicones, the
application areas continue to expand, forming a unique and important
product system in the field of new chemical materials. Many varieties
are irreplaceable and indispensable for other chemicals.
6. Silicon can increase the hardness of plant stalks and increase the
difficulty of feeding and digesting by pests. Although silicon is not an
essential element in the growth and development of plants, it is also a
chemical element necessary for plants to resist adversity and regulate
the relationship between plants and other organisms.
.

Silicon is a chemical element, its chemical symbol is
Si, formerly known as silicon. The atomic number is 14, the relative
atomic mass is 28.0855, there are two allotropes of amorphous silicon
and crystalline silicon, belonging to the third period of the periodic
table, the metal-like element of the IVA group. Silicon is also a very
common element, but it rarely appears in nature as a simple substance,
but in the form of complex silicate or silica, which is widely present
in rocks, gravel, and dust. The reserves of silicon in the universe rank
eighth. In the earth's crust, it is the second most abundant element,
constituting 26.4% of the total mass of the earth's crust, second only
to the first oxygen (49.4%).
Application field
1. High-purity single crystal silicon is an important semiconductor
material. A small amount of group IIIA element is added to
monocrystalline silicon to form a p-type silicon semiconductor; a small
amount of group VA element is added to form an n-type semiconductor. The
p-type semiconductor and the n-type semiconductor are combined to form a
p-n junction, which can be made into a solar cell, which converts
radiant energy into electrical energy. It is a promising material in the
development of energy. In addition, the widely used diodes, triodes,
thyristors, field effect transistors and various integrated circuits
(including chips and CPUs in people's computers) are all made of
silicon.
2. Metal ceramics, important materials for space navigation. Ceramic and
metal are mixed and sintered to make a metal-ceramic composite material,
which is resistant to high temperature, rich in toughness, and can be
cut. It not only inherits the respective advantages of metal and
ceramic, but also makes up for the inherent defects of the two. It can
be used in the manufacture of military weapons. The first space shuttle
"Columbia" was able to withstand the high temperature generated by
friction when traveling through dense atmosphere at high speed, thanks
to its shell made of 31,000 silicon tiles.
3. Optical fiber communication, the latest modern communication method.
Pure silica can be used to draw high-transparency glass fibers. The
laser can be transmitted forward through countless total reflections in
the path of the glass fiber, instead of bulky cables. The optical fiber
communication capacity is high. A glass fiber as thin as a hair can
transmit 256 telephones at the same time; and it is not affected by
electricity or magnetism, is not afraid of eavesdropping, and has a high
degree of confidentiality. Optical fiber communication will
revolutionize human life in the 21st century.
4. Silicone organic compounds with excellent performance. For example,
silicone plastic is an excellent waterproof coating material. Spraying
silicone on the walls of the subway can solve the problem of water
seepage once and for all. Coating a thin layer of silicone plastic on
the surface of ancient cultural relics and sculptures can prevent moss
from growing and resist wind, rain, and weathering. The Monument to the
People's Heroes on Tiananmen Square is treated with silicone plastic, so
it will always be white and fresh.
5. Due to the unique structure of organic silicon, it combines the
properties of inorganic materials and organic materials. It has basic
properties such as low surface tension, low viscosity-temperature
coefficient, high compressibility, and high gas permeability. It also
has high and low temperature resistance, electrical insulation, and
resistance. Excellent properties such as oxidation stability, weather
resistance, flame retardancy, water repellency, corrosion resistance,
non-toxicity and tastelessness, and physiological inertness. It is
widely used in aerospace, electronic and electrical, construction,
transportation, chemical, textile, food, light industry, medical, etc.
In the industry, silicones are mainly used in sealing, bonding,
lubrication, coating, surface activity, mold release, defoaming, foam
suppression, waterproofing, moisture-proof, inert filling, etc. With the
continuous growth of the number and variety of silicones, the
application areas continue to expand, forming a unique and important
product system in the field of new chemical materials. Many varieties
are irreplaceable and indispensable for other chemicals.
6. Silicon can increase the hardness of plant stalks and increase the
difficulty of feeding and digesting by pests. Although silicon is not an
essential element in the growth and development of plants, it is also a
chemical element necessary for plants to resist adversity and regulate
the relationship between plants and other organisms.
.
|
|
|